
SALT is a semantic-based adaptive platform for the evaluation of e-government services which allows each citizen to put emphasis in quality dimensions related with the problems she faces depending on her skills and expectations. Questions are structured into the two levels of the QUONTO model and ontology: level 1 for quality factors; and level 2 for quality dimensions.
In order to enable formal specification and analysis of the quality model: all factors that influence quality as well as the relationships between them have been defined formally and explicitly in the QUONTO ontology which formalizes all the knowledge needed for the realization of an adaptive evaluation of e-government services.
##Description:
SALT is a semantic-based adaptive platform for the evaluation of e-government services which allows each citizen to put emphasis in quality dimensions related with the problems she faces depending on her skills and expectations. Questions are structured into the two levels of the QUONTO model and ontology: level 1 for quality factors; and level 2 for quality dimensions.
In order to enable formal specification and analysis of the quality model: all factors that influence quality as well as the relationships between them have been defined formally and explicitly in the QUONTO ontology which formalizes all the knowledge needed for the realization of an adaptive evaluation of e-government services.
The SALT adaptive questionnaire is dynamically composed based on the problem and web page ontologies of QUONTO and across the following adaptation axes:
- Perception-based adaptation axis: The grade that the user gives to first level questions: If the grade is low, the relevant second level questions are presented
- Problem-based adaptation axis: The problems that the user faces during the navigation on the portal: If a problem has been identified, then the second level questions that are related with this problem are presented.For example a navigation problem is related with navigation questions
- Page metadata-based adaptation axis: The type of the pages visited by the user: Questions concerning specific portal’s parts will be presented only in case of a user session that includes these parts
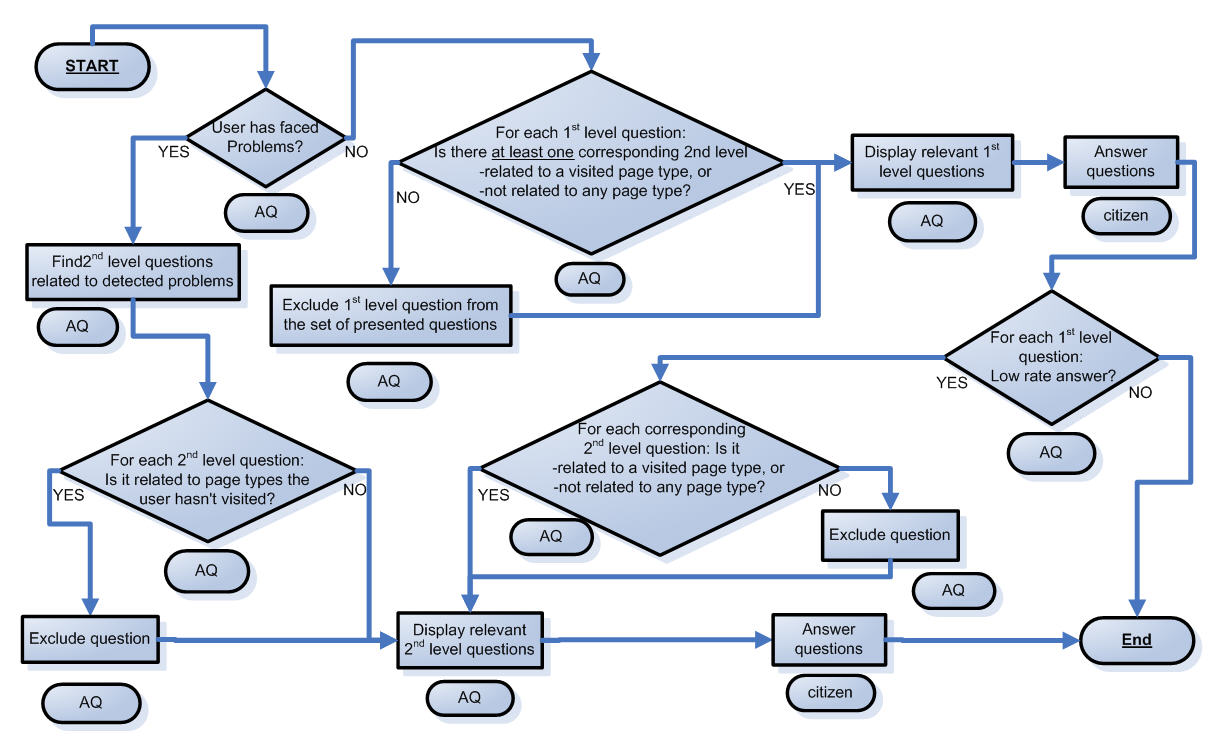
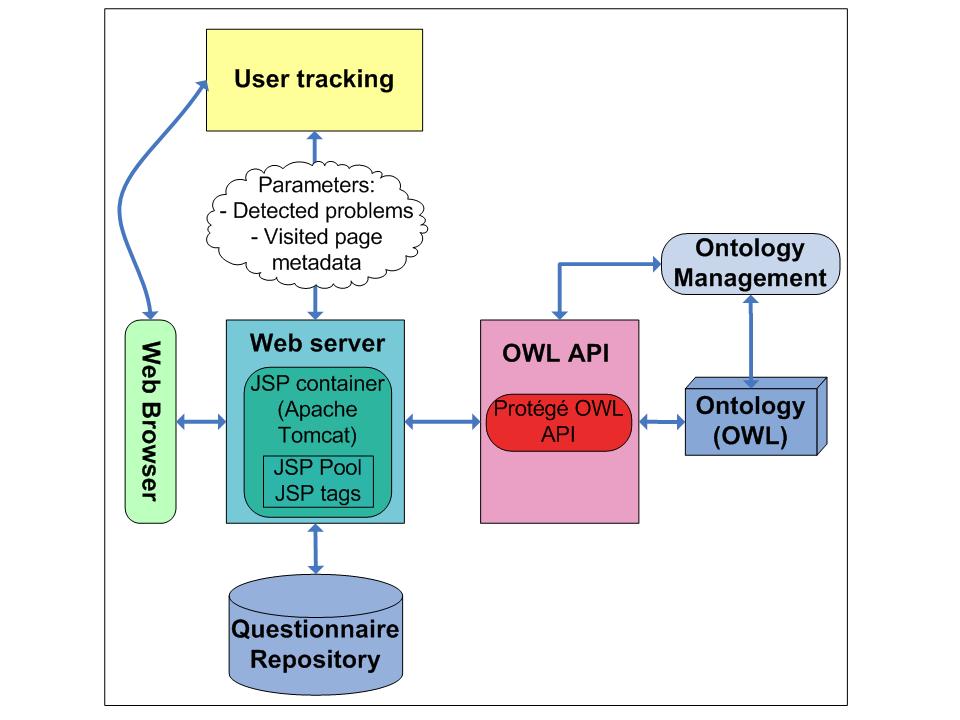
The figure above gives the SALT business logic, while the technical architecture of the tool is depicted in the figure below.
In order to enable the adaptation of SALT based on page metadata, the latter should first become available. This is achieved by annotating the portal’s pages with the pages types specified in the Web Portal ontology, by using an annotation editor tool. But page metadata alone are not sufficient for enabling SALT’s adaptation according to visited content.
There is also a need for a user tracking component which enables tracking user actions beyond simple click streams. This component tracks user interactions with the portal, builds a rich user model and provides parameters related to the user context to the SALT’s adaptation algorithm. The latter uses the user context in order to apply the problem-based and page metadata-based adaptation axes.
For designing the questionnaire templates we used the open source survey tool Web Survey Toolbox. This tool interacts with a MySQL questionnaire repository in order to store the questions as well as users’ answers. The system is hosted by an Apache Tomcat server.
The Web Survey Toolbox provides JSP tags in order to encapsulate business logic in the questionnaire presentation. We have used the predefined JSP tags and extended the JSP pages, in order to allow them to communicate with the ontologies that are used by the adaptation business logic, i.e. the Quality, Web Portal and Problem ontologies. As a Semantic Web Framework we used the Protégé OWL API which is an abstract layer above Jena.
##Publications:
For a review of state of the art see:
- Papadomichelaki X., Magoutas B., Halaris C., Apostolou D., Mentzas G., (2006), A Review of Quality Dimensions in E-government Services. In M. Wimmer et. al. (Eds.): EGOV 2006, Krakow, Poland, September 4-8 2006, Proceedings. LNCS 4084 Springer 2006, pp. 128–138. download paper
For the quality model, see:
- Halaris C., Magoutas B., Papadomichelaki X., Mentzas G., (2007), Classification and Synthesis of Quality Approaches in E-government Services. Internet Research: Electronic Networking Applications and Policy, Volume 17, Number 4, 2007 , pp. 378-401(24) download paper
For the ontology used in SALT, see:
- Magoutas, B., Halaris C., Mentzas G., (2007), An Ontology for the Multi-perspective Evaluation of Quality in E-Government Services. In M. Wimmer et. al. (Eds.): EGOV 2007, Regensburg, Germany, September 3-7, 2007, Proceedings. LNCS 4656 Springer 2007, pp. 318-329, download paper .
The SALT system is described in:
- Magoutas B., Chalaris C., Mentzas G., (2008) A Semantically Adaptive Interface for Measuring Portal Quality in e-Government. In C. Mourlas and P. Germanakos (Eds.): Intelligent User Interfaces: Adaptation and Personalization Systems and Technologies, Hershey, PA: IGI Global, download paper .
- Magoutas B., Schmidt K.U, Mentzas G., Stojanovic L., (2008), Using Ontologies in an Adaptive Interface for Measuring User Perceived Portal Quality. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, submitted for publication
Videos
SALT Demo 1
SALT Demo 2
##Downloads:
SALT is a sourceforge project available here

