March 2002–August 2004


1. Project description
Knowledge exchange between various experts is one of the key drivers of the information society. Therefore, all kind of possibilities to share knowledge in anefficient way have to be taken into account in order to be competitive in an increasingly knowledge-driven economy.
INKASS, is a holistic solution for Knowledge Trading comprising:
- an innovative approach to knowledge trading,
- a modular method that guides companies undertaking the journey towards knowledge trading,
- a robust system, which integrates content management with advanced search and retrieval, collaboration and communication facilities with e-commerce functionalities.
##Approach
Knowledge springs from knowledgeable people and thus itsnature is primarily tacit. But tacit knowledge can be made explicit by writingit down and putting it into a certain context which enables the knowledgereceiver to learn and understand the explicated knowledge and thus generate new tacit knowledge for him. Explicit knowledge can be encapsulated in information objects. By the creation of such information objects it is possible to tradeknowledge on a knowledge marketplace. Core to our approach is the assumption that:
Knowledge sharing and trading organisations support the exchange of information objects, which provide direct or indirect means to face challenges, solve problems and tasks
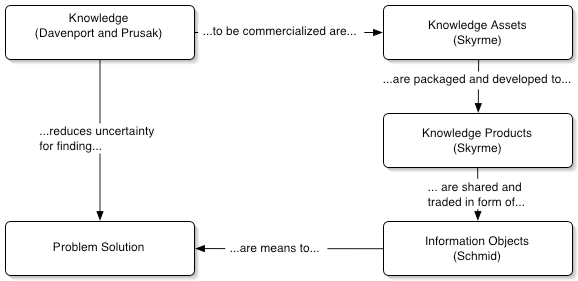
###Relationship of Terms
This relationship between knowledge and the solution of problems, tasks, and challenges show that knowledge exchange scenarios are present in the everydaylife of any organisation. But the way of how knowledge is exchanged within orbetween organisations highly depends on the network environment theseorganisations are embedded in. But in a general knowledge trading scenario theknowledge receiving agent needs to acquire information to help him finding asolution to a given challenge, task, or problem. He sends a request for asolution to other agents who might provide useful knowledge to him. Theseagents can offer a solution either themselves or take the position of anintermediary to call other agents for delivering an appropriate solution. Theycan ask for a complete solution or use a divide and conquer approach to dividethe problem into sub-problems to merge several answers into an overall solution. But the way knowledge is exchanged highly depends on the community,knowledge is shared in. For example between friends and colleagues knowledge isexchanged in a highly informal way, mostly mouth by mouth. The more thecommunity grows and external persons are involved the less knowledge isexchanged via thus methods and new ways of knowledge sharing have to be found.Therefore a classification of the business communities is needed in order toidentify the potential of knowledge sharing and knowledge trading within and between organisations.
##Methodology
The design, implementation and running of a knowledge marketplace can be separated into mainly three phases. In the first phase thewhole environment of the knowledge marketplace is analysed and the requirements for the knowledge marketplace are defined. Next the knowledge marketplace itself is set up and in a third phase the running system is continuouslyevaluated, improved and maintained.
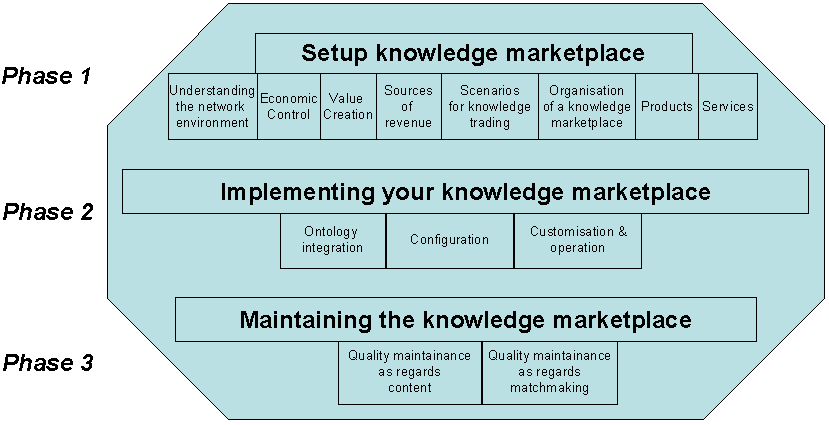
##Overview of the INKASS Methodology
###Software architecture
The following figure depicts an architectural overviewof the INKASS system in terms of the INKASS system services being used and howthey interact:
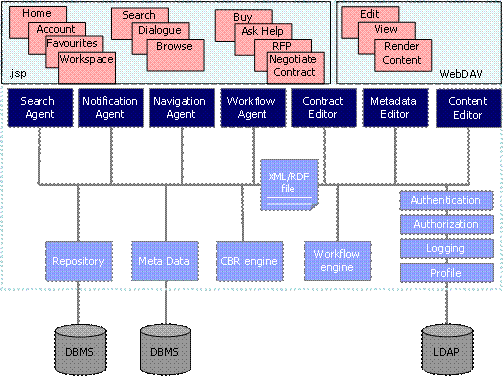
##Overview of INKASS SYSTEM services
For the details of the services the reader is referredto more technical documentation. We will address the functions that these services provide in terms of the functionality and features of the INKASS system.
Core services (in light blue) implement low level functionalities, such as security, document storage and metadata management.
Higher level agents (in dark blue) combine the functionalities provided by the core services in that they already implement some business logic that is typical for the application domain. As an example consider the processes involved when checking in a new document version which will internally involve various steps, such as storage versioning, search index update etc.
Application-specific components (in red), finally, provide the functionality that is needed for a particular application and also implement the layout and behaviour of the GUI.
##INKASS cases
The INKASS knowledge marketplace system has been tested and used by the following corporations.
- The Welding Institute, a research and technology organisation
- Planet SA, a management consultancy company
- The Athens Chamber of Commerce and Industry
#2. Related publications
- Apostolou, D., G. Mentzas and W.Maas KnowledgeNetworking for Collaborative Commerce Chapter VII in E. Y. Li and T. C. Du(eds) Advances in Electronic Business, Vol. 1, Theme: "CollaborativeCommerce", Idea Group Publishing, pp. 183-221
- Apostolou,D., G. Mentzas, A. Abecker, W.-C. Eickhoff, W. Maas, P. Georgolios, K. Kafentzis and S. Kyriakopoulou Challenges and Directions inKnowledge Asset Trading International Journal of Intelligent Systems inAccounting, Finance & Management, Vol. 13, 1-15 (2005)
- Kafentzis, K., G. Mentzas, D. Apostolouand P. Georgolios KnowledgeMarketplaces: Strategic Issues and Business Models Journal of KnowledgeManagement, Vol 8, No 1, pp. 130-146
- Kafentzis, K., D. Apostolou andG. Mentzas Inter-OrganizationalKnowledge Management Systems: Typology And Cases ECIS 2004, The 12th EuropeanConference on Information Systems, Turku Finland,June 14-16. 2004
- Apostolou,D., P. Georgolios, B. Klein, J. Franz, W. Maass, A. Abecker, K. Kafentzis, G. Mentzas Towards provision of knowledge-intensive products and services over theWeb IASTED International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Applications(AIA 2004), February 16 to February 18, 2004, in Innsbruck,Austria
- Mentzas, G.N., D. Apostolou andK. Kafentzis Inter-organisationalKnowledge Sharing and Trading Presented at the eChallenges 2003 Conference,Bologna, Italy, 22-24-October 2003
- Apostolou, D., K. Kafentzis, G.Mentzas, W. Maas KnowledgeNetworking in Extended Enterprises Presented at the ICE 2003 – 9thInternational Conference of Concurrent Enterprising, Espoo, Finland,16-18 June 2003
- Abecker, A., D. Apostolou, W.Maas, G. Mentzas, C. Reuschling, S. Tabor Towards an Information Ontology forKnowledge Asset Trading Presented at the ICE 2003 – 9th InternationalConference of Concurrent Enterprising, Espoo, Finland, 16-18 June 2003
#3. Project website
Visit INKASS Website

